Publications
Highlights
(For a full list see Google Scholar).
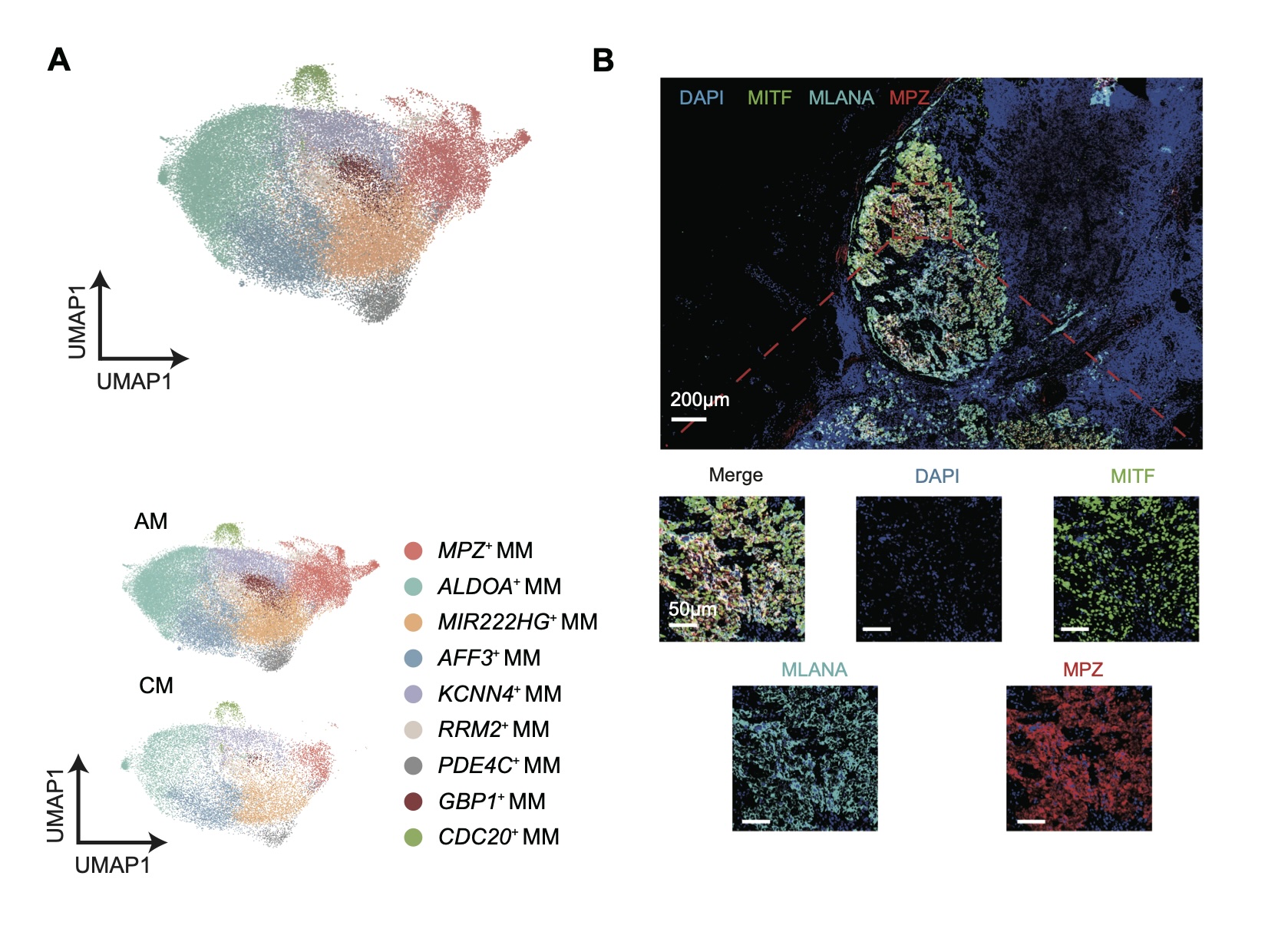
We conduct a comparative analysis between acral melanoma and cutaneous melanoma in single-cell transcriptomic level, revealed and characterized MPZ+ melanoma as an AM-specific melanoma that is related to worse prognosis in AM.
Hongyue Zhao *, Jie Tian *, Hang Li ^, and Binbin Lai^
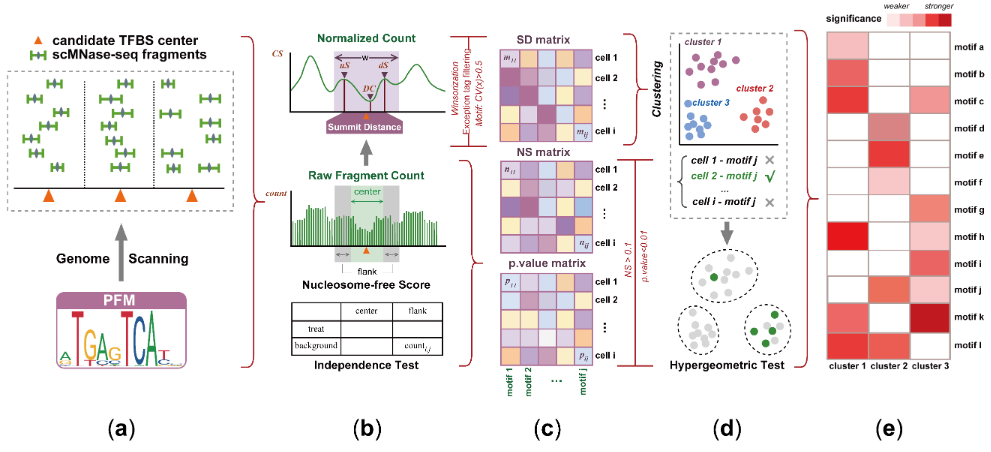
We present presents scNucMap, a tool designed for scMNase-seq data to map candidate nucleosome-free regions (NFRs), showing superior cell clustering performance over Signac and chromVAR across diverse samples. scNucMap identifies transcription factors associated with nucleosome depletion at CREs for cell-type annotation and regulatory network inference, and its application to scATAC-seq enriches nucleosome architecture analysis, demonstrating cross-modality versatility.
Qianming Xiang and Binbin Lai
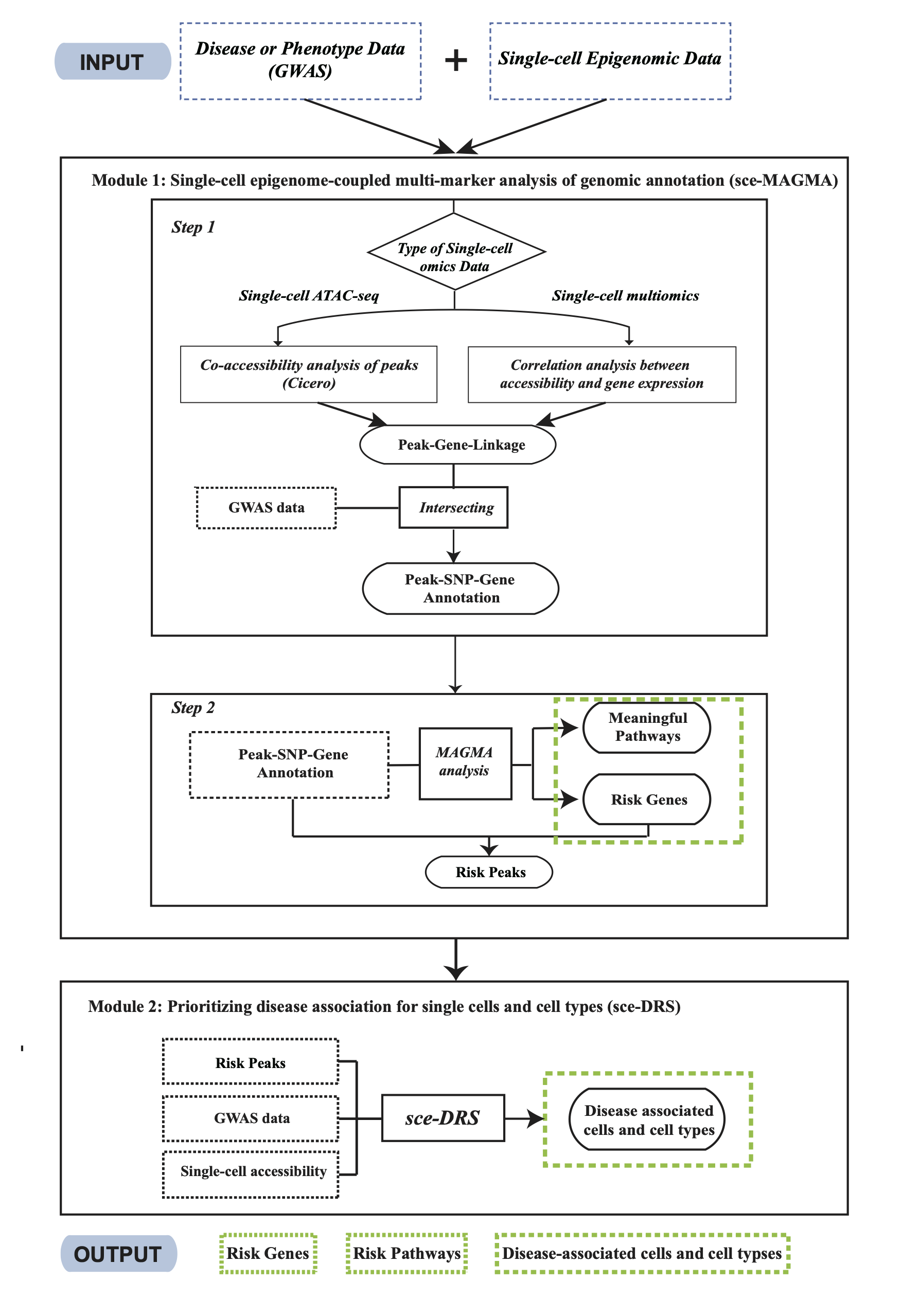
We present SC-VAR, a novel computational tool designed to enhance the interpretation of disease-associated risks from GWAS using single-cell epigenomic data. SC-VAR leverages single-cell epigenomic data to predict functional outcomes including risk genes, pathways, and cell types for both coding and noncoding disease-associated variants.
Gefei Zhao and Binbin Lai
Briefings in Bioinformatics (2025)
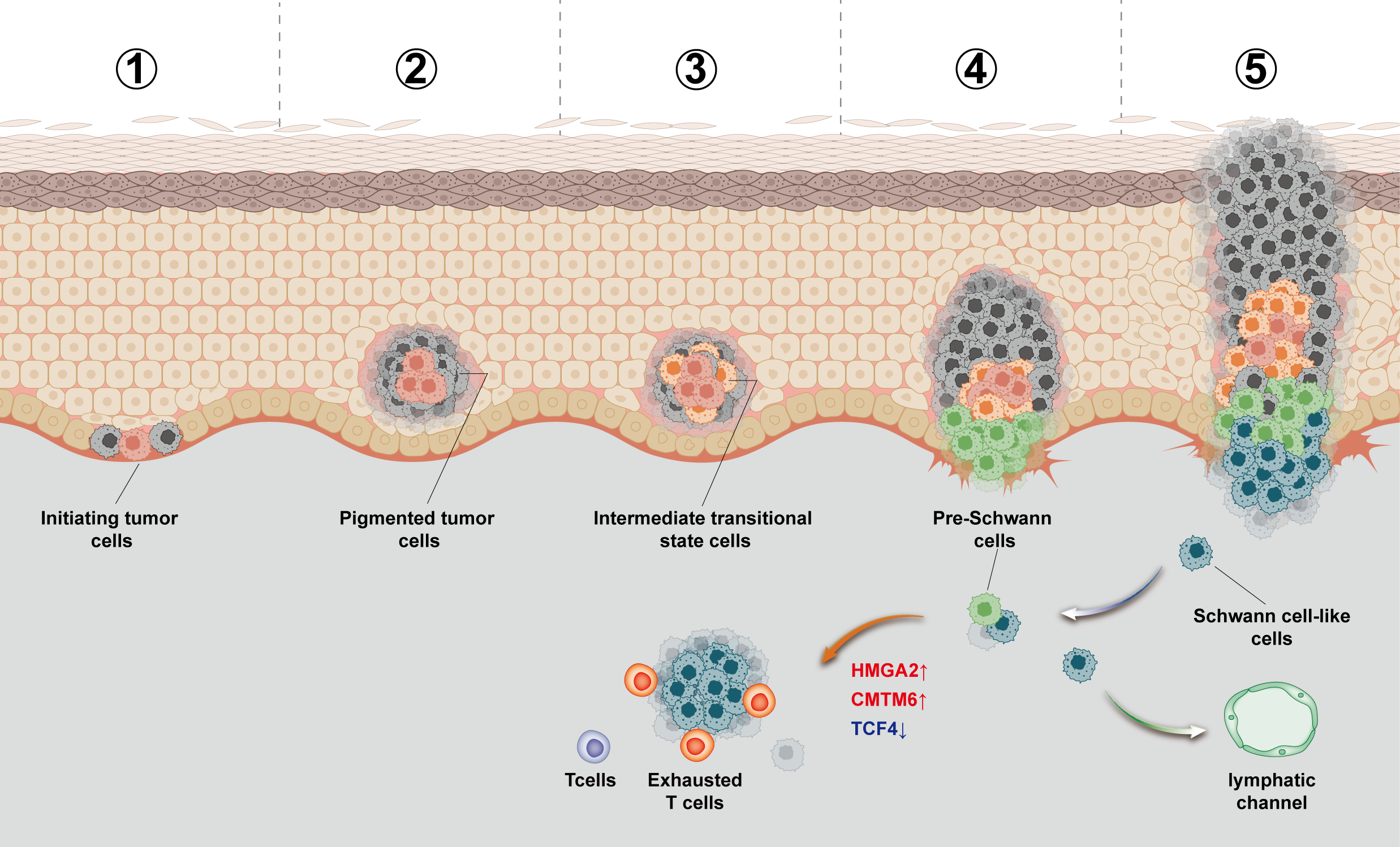
A thourough characterization of Schwann-like subtype of planter melanoma which is related to worse progression and poor prognosis. A novel TF HGMA2 was reported to play an important role in regulate the subtype.
Jie Tian *, Lu Zhang *, Le Zhuang, Pingping Lin, Shenxi Zhang, Yicen Yan, Yu Yang, Guohong Zhang ^, Hang Li ^, and Binbin Lai ^
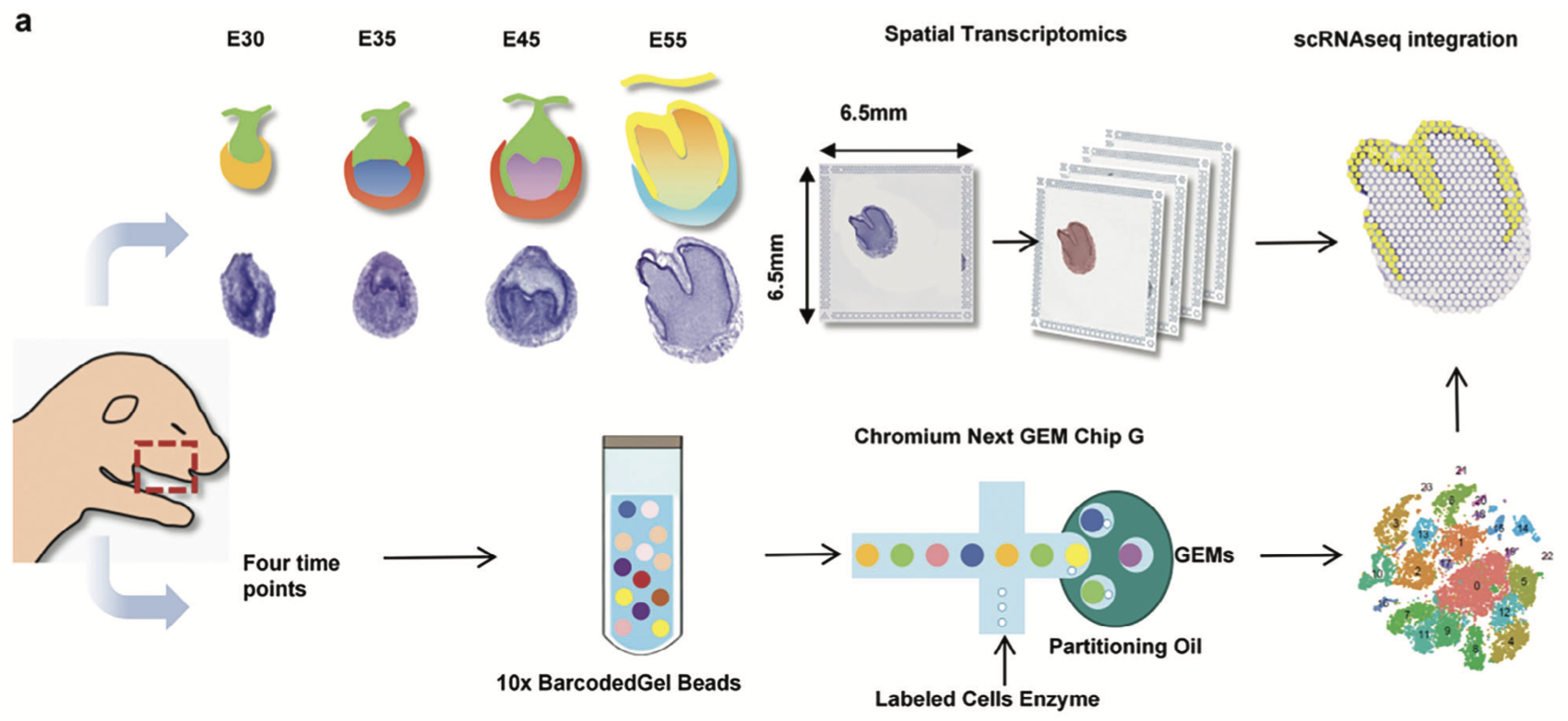
We described an cellular atlas for characterizing the tooth morphogenesis using both single-cel RNA-seq and spatio transcriptome techniques.
Shengjie Jiang, Yuning Zhang, Huimin Zheng, Kai Zhao, Yue Yang, Binbin Lai ^, Xuliang Deng ^, and Yan Wei ^
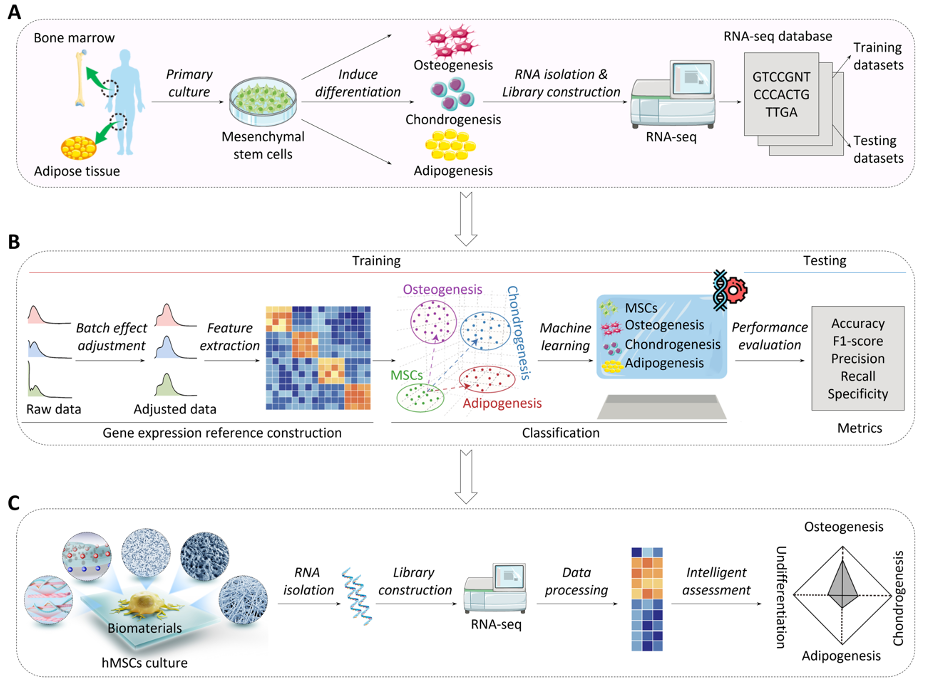
We report a computational framework for biomaterial-induced cell lineage fate prediction, termed MeD-P. We demonstrate that MeD-P is an efficient and accurate strategy for stem cell lineage fate prediction and preliminary biomaterial functional evaluation.
Yingying Zhou *, Xianfeng Ping *, Yusi Guo *, Boon Chin Heng, Yijun Wang, Yanze Meng, Shengjie Jiang, Yan Wei, Binbin Lai ^, Xuehui Zhang ^, Xuliang Deng ^
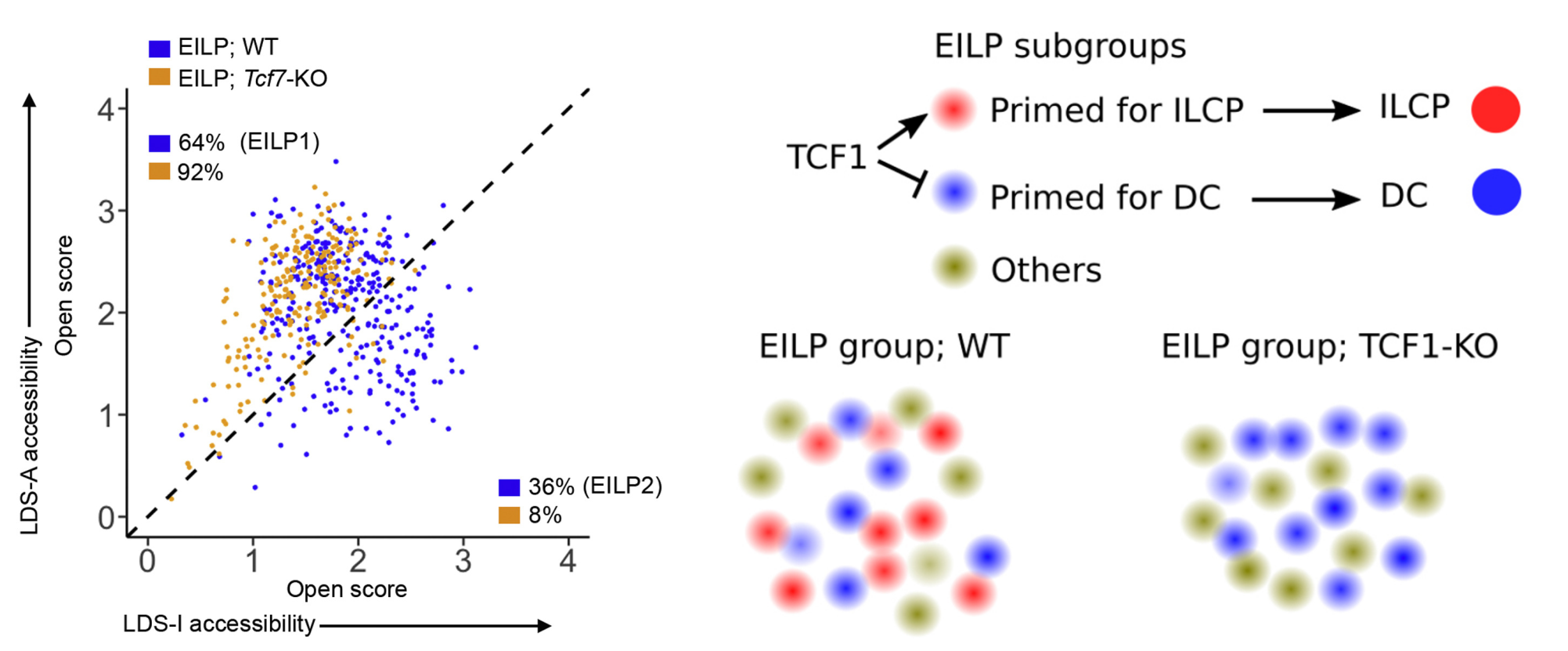
Using multiple advanced epigenomic sequencing technologies, we report the celular heterogeneity on epigenome in early innate lymphoid progenitors which affects the downstream lineage differentiation. We show how key transcription factor TCF1 regulate the epigenomic heterogeneity and differentiation towards ILC progenitors.
Ren G *, Lai B *, Harly C, Baek S, Ding Y, Zheng M, Cao Y, Cui K, Yang Y, Zhu J, Hager GL, Bhandoola A, Zhao K.
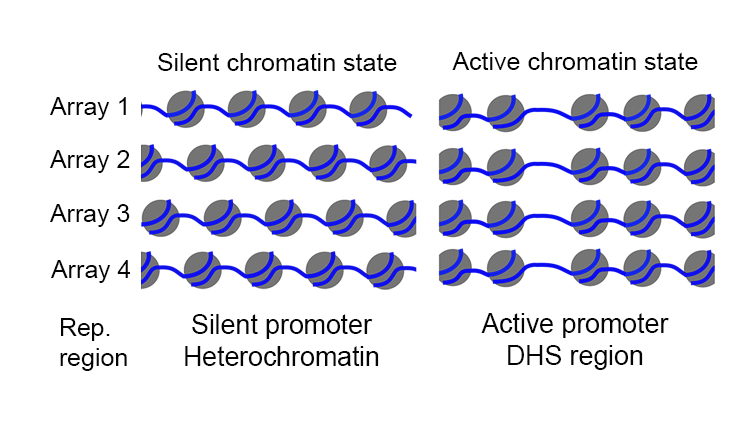
We report a technique, termed single-cell micrococcal nuclease sequencing (scMNase-seq) that can be used to simultaneously measure genome-wide nucleosome positioning and chromatin accessibility in single cells. We reveal novel principles of nucleosome organization related to chromatin activity and report the existence of cells primed for differentiation to specific lineages in undifferentiated cell populations.
Lai B, Gao W, Cui K, Xie W, Tang Q, Jin W, Hu G, Ni B, Zhao K
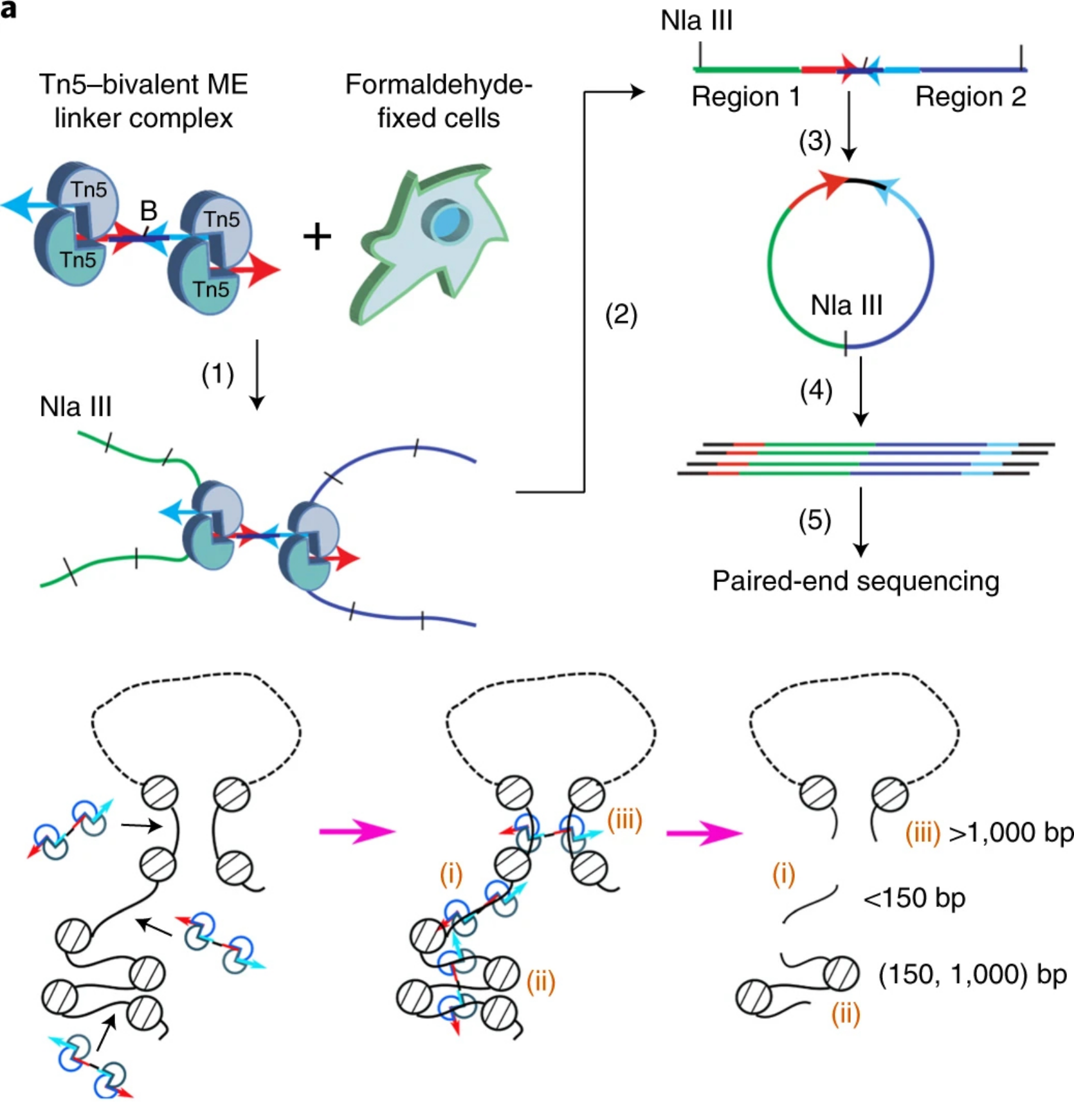
We report transposase-mediated analysis of chromatin looping (Trac-looping) for simultaneous detection of multiscale genome-wide chromatin interactions among regulatory elements and chromatin accessibility. Application of Trac-looping to human CD4+ T cells revealed substantial reorganization of enhancer-promoter interactions associated with changes in gene expression after T cell receptor stimulation.
Lai B *, Tang Q *, Jin W *, Hu G *, Wangsa D, Cui K, Stanton BZ, Ren G, Ding Y, Zhao M, Liu S, Song J, Ried T, Zhao K